Aggression from a Great Dane is hostile behavior towards you, other people, or animals. You can feel aggression from your dog when they growl, snarl, tense their body, show the whites of their eye, and teeth, have intense eye contact or lean forward in readiness to lunge, nip or bite.
So, why is your Great Dane aggressive?
In this article we will get into the reasons behind Great Dane’s aggression and when to seek help.
Table of Contents
Why Is My Great Dane Aggressive?
A Great Dane being aggressive can be due to an underlying medical condition, fear, reactivity to situational stimuli, illness, injury, possessiveness, dominance, and leash reactivity. These factors can trigger aggression pushing them to direct hostile behavior towards their owners, other people, or animals.
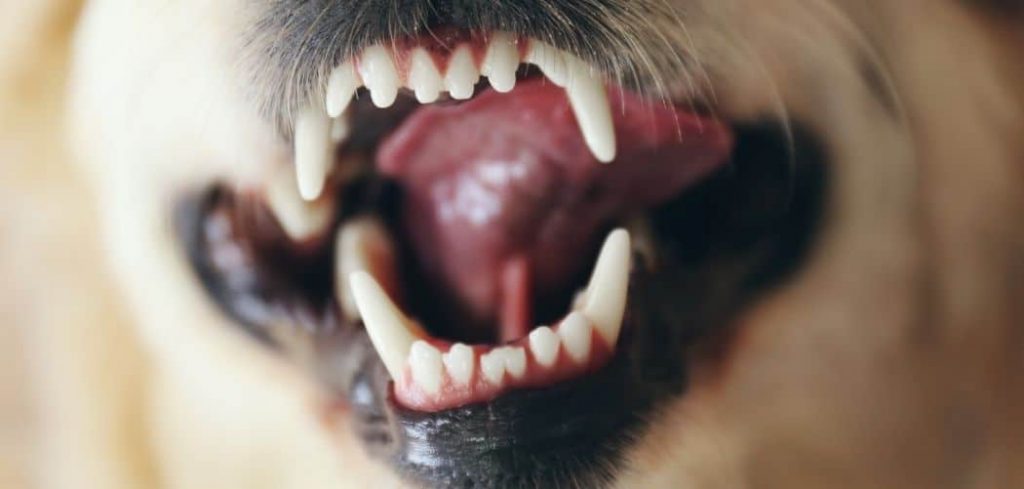
Causes of Aggression in Great Danes
Underlying medical condition
An underlying medical problem can cause a Great Dane to be aggressive to the pain and discomfort.
These health problems include hypothyroidism, neurological problems such as brain tumors, epilepsy, or encephalitis among other health conditions that can trigger aggression.
Injury to any part of a dog’s body can also make your dog irritable, growl, and refuse to be touched when approached. They may respond with aggressive behavior because of the pain.
Fear
Fear may also trigger aggression from a Great Dane. It is a common cause of aggression and occurs when a Great Dane feels like they are in danger or trapped with no escape.
Approaching them may lead to aggression because of the need to defend themselves. This can happen even if your actions and intentions were not aggressive towards them
Mistreatment from a previous owner can also cause them to be fearful of you or people and in this case, may act aggressively.
Related: Do Great Danes attack?
Reactivity to situations or stimuli
A Great Dane may react to a situation with aggression. This behavior usually is due to a lack of training and socialization to get along with people or animals.
They might be triggered for example by bearded men, small children, other pets in the home, or even an innocent gesture from you which can be perceived negatively.
Injury
Sudden aggression is mainly due to injuries when a Great Dane gets hurt on any part of their body which can include bone fractures, broken bones, cuts, or internal injury.
Possessiveness
It is quite natural for a dog to protect their owner, family, and property. Therefore a Great Dane may be aggressive because of resource guarding when they sense a threat to them from strangers.
They may also show possessiveness around their food or toys when around other pets, or people.
Related: Why Is My Great Dane So Annoying?
Dominance
A Great Dane being aggressive is also a sign of dominance over other dogs and also people. This can be displayed by nipping, biting, guarding their resources, or disobedience.
Frustration
Frustration may also lead a Great Dane to become aggressive especially when they are confined in an area such as a crate, chain link fence, or on a leash.
Leash reactivity is when a dog behaves in an unwanted manner when they are on a leash such as growling or barking due to frustration of wanting to be released. When released from the leash they would not have the behavior.
The frustration and aggression can be redirected to you when you approach your dog.
Recommended reading: Why is my Great Dane becoming aggressive? to learn more on sudden aggression.
When To Seek Help
When you notice aggressive behavior from your Great Dane, do not try to force engagement with them. Act calmly around them.
Take note of the surrounding circumstances and try to determine the possible reasons for the aggression. For example, if it is reactivity to a stimulus such as other people, or small children.
Know your Great Dane’s triggers or any other behavior change and share this with your veterinarian.
Seek medical consultation from a veterinarian so that they can rule out any medical problem. If there is no medical problem and the problem is a behavioral issue the veterinarian will recommend a certified animal behaviorist to assist in training to correct the behavior.
Treatment and Management
Treatment of Great Dane aggression varies depending on the underlying cause of the aggression. Interventions to manage aggression include:
Medication
Medication may be prescribed when illness, injury, or stress is determined to be the cause.
Adjustment of their environment
If Great Dane aggression is due to the situation or environment they’re in such as fear, and reactivity to situations such as small children or bearded men, minimize exposure to these stimuli.
Do not use punishment as a corrective measure
Punishment such as yelling or hitting should not be used towards an aggressive Great Dane.
This response will only aggravate them and they may defend themselves by lunging or biting.
This will also create mistrust between you and your dog and further lead them to undesired behavior.
Do not force engagement
Also when you notice your Great Dane starting to be aggressive with signs such as growling, snarling, tensing their body, or being irritable, do not approach them at the moment or force interaction.
This can lead to hostility from them. Contact your veterinarian and explain the surrounding circumstances so that the underlying cause of the Great Dane aggression can be determined.
Takeaway
Great Dane aggression is a behavior triggered by underlying factors that cause a Great Dane to respond with hostility.
Investigate and assess the situation around your dog that may be causing their hostile behavior such as fear, illness, territorial aggression, or dominance to act appropriately to help the situation.
In case of illness or when you’re not sure of the cause of the aggression, always contact your veterinarian for guidance.
